- Skincare products: enhanced moisturization, essence absorption, and in-depth penetration
- Skin cleansing products: enhanced in-depth cleansing
Bio-Cellulose Nanofiber (Bio-CNF)
1.Outperforming transdermal absorption
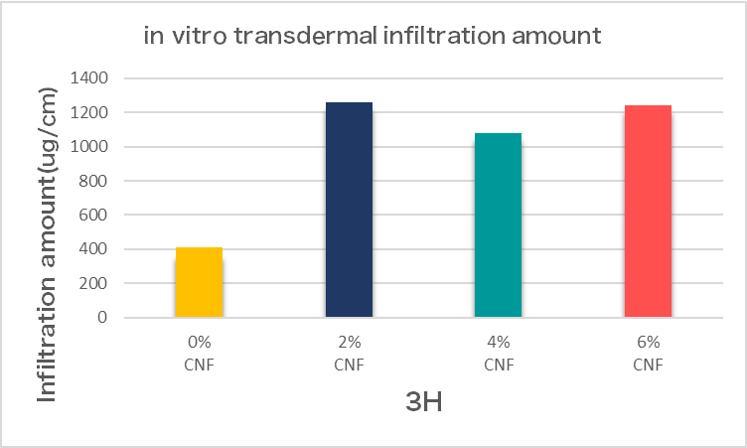
Empirical testing of Bio-CNF showed that the transdermal absorption amount of berberine added with Bio-CNF was up to 4 times more than berberine without Bio-CNF, achieving the effects of effective absorption and in-depth penetration.
Varying in-vitro transdermal infiltration amounts of berberine (ug/cm2)(n=2) in 3 hours. Compared with the medicine without Bio-CNF, the transdermal infiltration amounts of the medicinal ingredients of those with Bio-CNF increased obviously by 4 times in 3 hours.
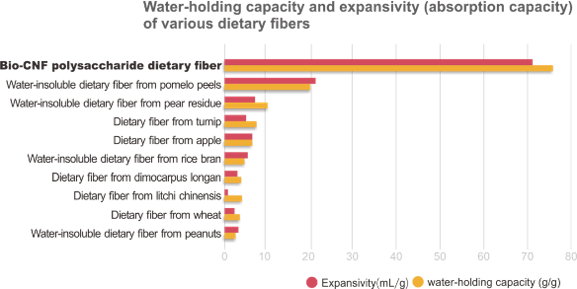
- Super excellent water holding capability and expansivity: even a small amount can increase daily intake of dietary fiber and avoid intestinal diseases.
- Nanoscale cellulose can powerfully suppress glucose, cholesterol and fatty acid, keeping 3 highs away.
- Effectively inhibiting Alpha-Amylase, and thus preventing intestinal sugar from breakdown and absorption.
- Small molecules can penetrate intestinal wall cells to increase insulin sensitivity, so as to keep diabetes away.
- Remarkably increasing specific surface area to enhance toxin adsorbing capability.
- Polysaccharide dietary fiber outperforms all other dietary fibers, about 4~35 times more effective than other dietary fibers.
- Greater absorption capability helps polysaccharide dietary fiber bring better effects.
3. 3D structured liquid dressings
Monobacterial Bio-CNF dressings are a highly desirable type of dressings. Their good hydrophilicity, antibacterial properties and excellent biocompatibility have demonstrated obvious advantages over conventional dry dressings and other novel dressings in facilitating wound healing.
- The unique ultra-fine nanofiber porous structure of monobacterial Bio-CNF provides good air and water permeability and strong capability of moisture absorption, which could protect wounds from microorganism infection.
- The superior mechanical strength enables our dressings to exert certain pressure on wound surface when applied thereon, which expedites drainage of exudate, elimination of oedema and wound healing. The ultra-fine pore size prevents growth of cells into the dressing, and thus reduces secondary damage to wound surface caused by dressing changes.
- Free from cytotoxicity, sensitization and irritation, in line with the basic biological requirements for wound dressings.
- Stable chemical structures and low degradability make the toxicity and metabolic reactions of the degradation products negligible. With no need for cleansing wounds, dressing changes are made easier.
- Applications of monobacterial Bio-CNF in medical materials are in line with modern wound healing theory. Thus, Bio-CNF is a wound repair material of great potential.
4.Diverse Industrial Additives
Bio-CNF demonstrates extensive industrial applications as it can work not only as a modifier, but as a disperser, homogenizing agent and reinforcing agent.
- Under the entrustment of EVO PHANCIE, Taiwan Textile Research Institute conducted tests, and the results show that when being added to aqueous PU resin at a ratio of 0/0.6/1.0/5.0/10/30%, Bio-CNF contributed positively to the strength of the PU film, and remarkably enhanced the extensibility of the PU film.
- The addition of Bio-CNF significantly improved the mechanical performance of cement-based composite materials. For Bio-CNF to be added, a mass fraction of 0.02% was the best parameter in experiments, whereby the flexural strength and the compressive strength of the materials increased by 20% and 8%, respectively.
- Bio-CNF has a large specific surface area, strong hydrogen chain bonding ability, and excellent membrane-forming properties. As a result, Bio-CNF can be used as adhesive, thickening and suspending agents. Bio-CNF at a low concentration can produce a viscous suspension. Bio-CNF is able to achieve the same viscosity when at a lower concentration than other thickening agents. The resultant solution can be poured, pumped or sprayed, having broad application prospects as an adhesive and thickening agent used in the wet end of a papermaking machine.